Content
Add/Remove Windows 8/8.1 Features
Open the Windows 8/8.1 Features Window
GUI of Add/Remove Windows 8.1 Features
Steps of Open Windows Features Window
List of Windows 8.1 Features
Add/Remove Windows 8/8.1 Features
Some additional Windows 8.1 features can be turn on or off through the Windows features window
Open the Windows 8/8.1 Features Window
There are more than one way to open the Windows 8/8.1 Features Window
In Windows 8.1, go to the Start screen and search for the words “add remove”. Click or tap "Add or remove programs"in the list of search results
Alternatively, you can open the Control Panel and click or tap on the "Uninstall a program" link, found in the Programs section. Then, click or tap on "Turn Windows features on or off" and the Windows Features window will open.
GUI of Add/Remove Windows 8.1 Features
Steps of Open Windows Features Window
- Open the "Control Panel" window from the "settings" charm of the right edge
charms bar. Click "Programs" to open the "Programs" window
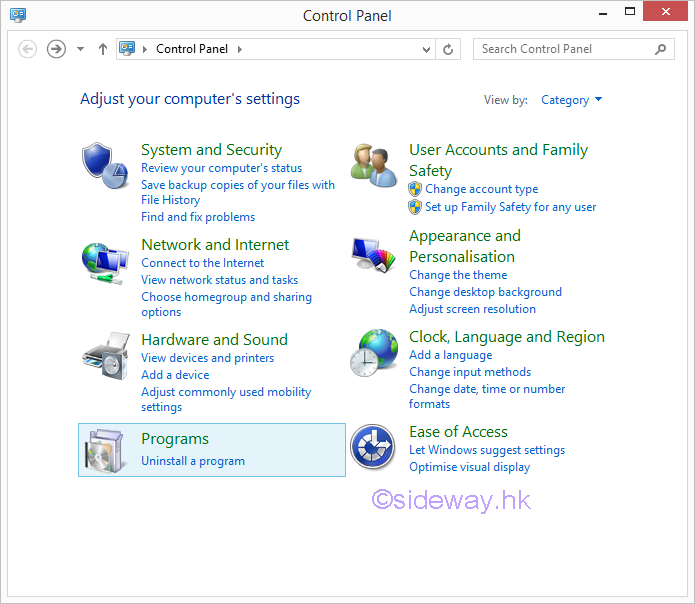
- Click "Turn Windows features on or off" under "Programs and Features to open the "Windows
Features" window.

- Click the checkbox to turn the corresponding feature to on or off.
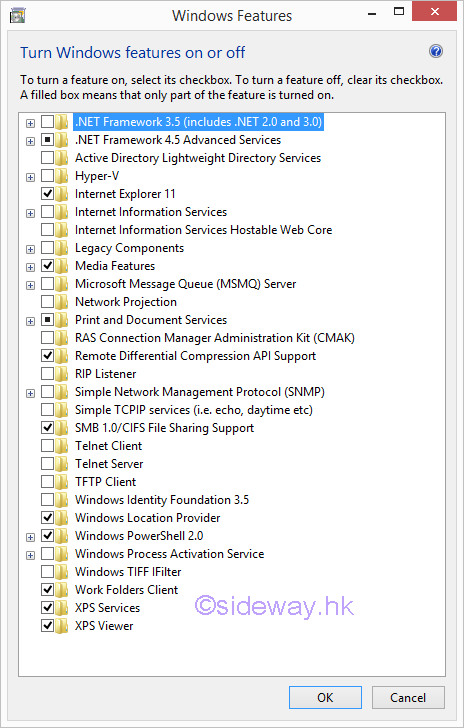
List of Windows 8.1 Features
The available features for turning on or off
- .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0)
A software development framework developed by Microsoft. This is provided because the .NET Framework 4.5 included by default is not backwards compatible with version 3.5 or older versions. - .NET Framework 4.5 Advanced Services
The advanced services include ASP.NET 4.5 (a server-side web application framework) and WCF Services and is used for implementing and deploying service-oriented architectures and distributed computing services.
WCF Services and TCP Port sharing are the two defaults that come with Windows. - Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services
A light-weight version of Active Directory Domain Services. This feature's purpose is to provide only the directory services. A scenario in which it can be used is when you have applications that need to have access to a directory service but they do not need to access an Active Directory database. - Hyper-V
A Windows feature, similar to VirtualBox or VMware, for running virtual machines. The processes of Hyper-V are run at a lower level in the operating system closer to the physical layer (the actual hardware). - Internet Explorer 11
The default Internet browser from Microsoft that comes with Widnows. - Internet Information Services
The IIS of Windows 8.1 which is a web server used to host web sites. - Internet Information Services Hostable Web Core
A light-weight version of IIS which a low-level component used to run Web applications. - Legacy Components
A deprecated DirectPlay API that was a part of the DirectX application programming interface. It used to be a library designed for network communication. - Media Features
The default media feature is the Windows Media Player from Microsoft that comes with Windows. - Microsoft Message Queue (MSMQ) Server
MSMQ is an old service to improve communications when connecting with unreliable networks. - Network Projection
A feature that allows Windows users to remotely use projectors that are connected to the network for delivering a presentation. - Print and Document Services
Services that are to use and manage printing, faxing and scanning devices. Windows Fax and Scan allows you to use faxes and scanners. The Internet Printing Client enables you to connect and print to a printer that's connected to the local network or the Internet. Other services like LPD Print Service and LPR Port Monitor are alternate printing technologies that became deprecated and are no longer used on a large scale. Scan Management is used for monitoring and managing network connected scanners.
The Internet Printing Client and Windows Fax and Scan services are the two defaults that come with Windows. - RAS Connection Manager Administration Kit (CMAK)
Feature that is used to create custom connections to remote servers and networks, protected by VPN. - Remote Differential Compression API Support
A synchronization algorithm that allows fast comparisons between synchronized files, which detects the data removed or added from their contents. This feature is used by some Windows programs and apps and is a default feature that comes with windows. - RIP Listener
A service that is used to listen for RIP announcements sent by routers and modify the routing table based on the information gathered. However, the routers your computer communicates with must support the RIPv1 protocol. - Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
A legacy protocol created for administering devices that are connected to a network. Using this rather old protocol you can manage devices like routers, printers, computers etc. - Simple TCP/IP services (i.e. echo, daytime, etc)
A collection of "oldies but goldies" command line tools that include character generator, daytime, discard, echo, and quote of the day. - SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support
A feature that is to enable the sharing of files and printers with computers running older versions of Windows, ranging from Windows NT 4.0 up to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 R2. The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol may be used by other operating systems like Linux or OS X to communicate with Windows devices.
The SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support feature is a default feature that comes with Windows. - Telnet Client
A legacy command line client that uses the Telnet network protocol to provide a bidirectional text-oriented communications with a Telnet server. - Telnet Server
A feature that is used to create a Telnet server which use the Telnet protocol to accept incoming connections. - TFTP Client
A simple command line tool that is used to transfer files via the Trivial File Transfer Protocol/ - Windows Identity Foundation 3.5
A software framework for building identity-aware applications. - Windows Location Provider
A feature that can use GPS sensors, IP address resolution, Wi-Fi triangulation or cell phone tower triangulation methods to establish geographical location data for desktop programs, apps and websites.
Windows Location Provider is a default feature that comes with Windows. - Windows Powershell 2.0
A command-line tool that focuses on task automation and configuration management.
Windows Powershell 2.0 is a default feature that comes with Windows. - Windows Process Activation Service
A service for message-based applications and components that's related to Internet Information Services (IIS). - Windows TIFF IFilter
A feature that is used to recognize text inside .TIFF image files. It is disabled by default, as optical character recognition has a big impact on performance. - Work Folders Client
A feature that allows users to sync a folder and its content, from the corporate network to their personal devices. Files created locally will sync back to the file server in the corporate environment.
Work Folders Client is a default feature that comes with Windows. - XPS Services
Services that is used to provide support for Microsoft's ".XPS" file format. This service provides functionality such as printing and saving of XPS files.
XPS Services is a default feature that comes with Windows. - XPS Viewer
A small application that is used to view and use ".XPS" files.
XPS Viewer is a default feature that comes with Windows..
source: http://www.digitalcitizen.life/what-are-those-windows-features-you-can-add-or-remove
©sideway
ID: 161000016 Last Updated: 10/14/2016 Revision: 0
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Sensoryscape(last updated On 1/5/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Resorts World Sentosa(last updated On 1/4/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa HarbourFront(last updated On 1/3/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa(last updated On 1/2/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight River Wonders(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Night Safari(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Curiosity Cove(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Imbiah(last updated On 12/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 36
Reference 79
Hardware 54
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
