Content
Powers of Natural Numbers Series[3]
First n Natural Numbers Series[1]
First n Natural Number Squares Series[3]
First n Natural Number Cubes Series[3]
Powers of Natural Numbers Series[3]
Powers of natural numbers series can also be found algebraically by making use of the power of a binomial.
First n Natural Numbers Series[1]
For the first n natural number series, 1+2+3+...+n, a binomial to the power of 2 can be used. By making use of the identity (n+1)2=n2+2n+1⇒(n+1)2-n2=2n+1. Let n=n-1 and substitute into the identity, then (n)2-(n-1)2=2(n-1)+1. By repeating the n=n-1 substitution, and get (n-1)2-(n-2)2=2(n-2)+1. By repeating the n=n-1 substitution again, and get (n-2)2-(n-3)2=2(n-32=2(n-3)+1. By continuing the n=n-1 substitution process until the original variable n is reduced to 1, that is ..., ((n-(n-2))+1)2-(n-(n-2))2=2(n-(n-2))+1, (1+1)2-(1)2=2(1)+1, a totally n sets of identities are obtained. By adding up all the identities, the left hand side is reduced to the first and last term, (n+1)2-12, while the right hand side remains the summation of all terms. After rearranging the similar terms on the right hand, the identity becomes (n+1)2-12=2(n+(n-1)+(n-2)+(n-3)+...+2+1)+n(1). Imply (n+(n-1)+(n-2)+(n-3)+...+2+1)=(((n+1)2-1)-n)/2=(n2+n)/2=n(n+1)/2. Imply

First n Natural Number Squares Series[3]
For the first n natural number squares series, 12+22+32+...+n2, a binomial to the power of 3 can be used. By making use of the identity (n+1)3=n 3+ 3n2+3n+1⇒(n+1)3-n3=3n2+3n+1. Let n=n-1 and substitute into the identity, then (n)3-(n-1)3=3(n-1)2+3(n-1)+1. By repeating the n=n-1 substitution, and get (n-1)3-(n-2)3=3(n-2)2+3(n-2)+1. By repeating the n=n-1 substitution again, and get (n-2)3-(n-3)3=3(n-3)2+3(n-3)+1. By continuing the n=n-1 substitution process until the original variable n is reduced to 1, that is ..., (n-(n-2)+1)3-(n-(n-2))3=3(n-(n-2))2+3(n-(n-2))+1, (1+1)3-(1)3=3(1)2+3(1)+1, a totally n sets of identities are obtained. By adding up all the identities, the left hand side is reduced to the first and last term, (n+1)3-13, while the right hand side remains the summation of all terms. After rearranging the similar terms on the right hand, the identity becomes (n+1)3-13=3(n2+(n-1)2+(n-2)2+(n-3)2+...+22+12)+3(n+(n-1)+(n-2)+(n-3)+...+2+1)+n(1). Imply (n2+(n-1)2+(n-2)2+(n-3)2+...+22+12) =((n+1)3-1-3(n+(n-1)+(n-2)+(n-3)+...+2+1)-n)/3=(n3+3n2+3n+1-1-n)/3-(n+(n-1)+(n-2)+(n-3)+...+2+1) =(n3+3n2+2n)/3-n(n+1)/2 =(2(n3+3n2+2n)-3(n2+n))/6 =(2n3+3n2+n)/6=(n(2n2+3n+1))/6=(n(n+1)(2n+1))/6. Imply

First n Natural Number Cubes Series[3]
For the first n natural number cubes series, 13+23+33+...+n3, a binomial to the power of 4 can be used. By making use of the identity (n+1)4=n 4+4n3+6n2+4n+1⇒(n+1)4-n4= 4n3+6n2+4n+1. Let n=n-1 and substitute into the identity, then (n)4-(n-1)4= 4( n-1) 3+6 ( n-1) 2+4 (n-1)+1. By repeating the n=n-1 substitution, and get (n-1)4-(n-2)4= 4 (n-2) 3+6 (n-2) 2+4 ( n-2)+1. By repeating the n=n-1 substitution again, and get (n-2)4-(n-3)4= 4 ( n-3) 3+6 (n-3) 2+4 ( n-3)+1. By continuing the n=n-1 substitution process until the original variable n is reduced to 1, that is ..., (n-(n-2)+1)4-(n-(n-2))4= 4(n-(n-2))3+6(n-(n-2))2+4(n-(n-2))+1, (1+1)4-(1)4=4 (1)3+6(1)2+4(1)+1, a totally n sets of identities are obtained. By adding up all the identities, the left hand side is reduced to the first and last term, (n+1)4-14, while the right hand side remains the summation of all terms. After rearranging the similar terms on the right hand, the identity becomes (n+1)4-14= 4(n3+(n-1)3+(n-2)3+(n-3)3+...+23+13)+6(n2+(n-1)2+(n-2)2+(n-3)2+...+22+12)+4(n+(n-1)+(n-2)+(n-3)+...+2+1)+n(1). Imply (n3+(n-1)3+(n-2)3+(n-3)3+...+23+13) =((n+1)4-1-6(n2+(n-1)2+(n-2)2+(n-3)2+...+22+12)-4(n+(n-1)+(n-2)+(n-3)+...+2+1)-n)/4=(n 4+4n3+6n2+4n+1-1-n)/4-6(n2+(n-1)2+(n-2)2+(n-3)2+...+22+12)/4-(n+(n-1)+(n-2)+(n-3)+...+2+1) =(n 4+4n3+6n2+3n)/4-n(n+1)(2n+1)/4-n(n+1)/2 =((n4+4n3+6n2+3n)- (2n3+2n 2+ n2+n) -2(n2+n))/4 =( n4+2n3+n2)/4=(n 2(n2+2n+1))/4=(n 2(n+1) 2)/4=((n(n+1))/2) 2. Imply
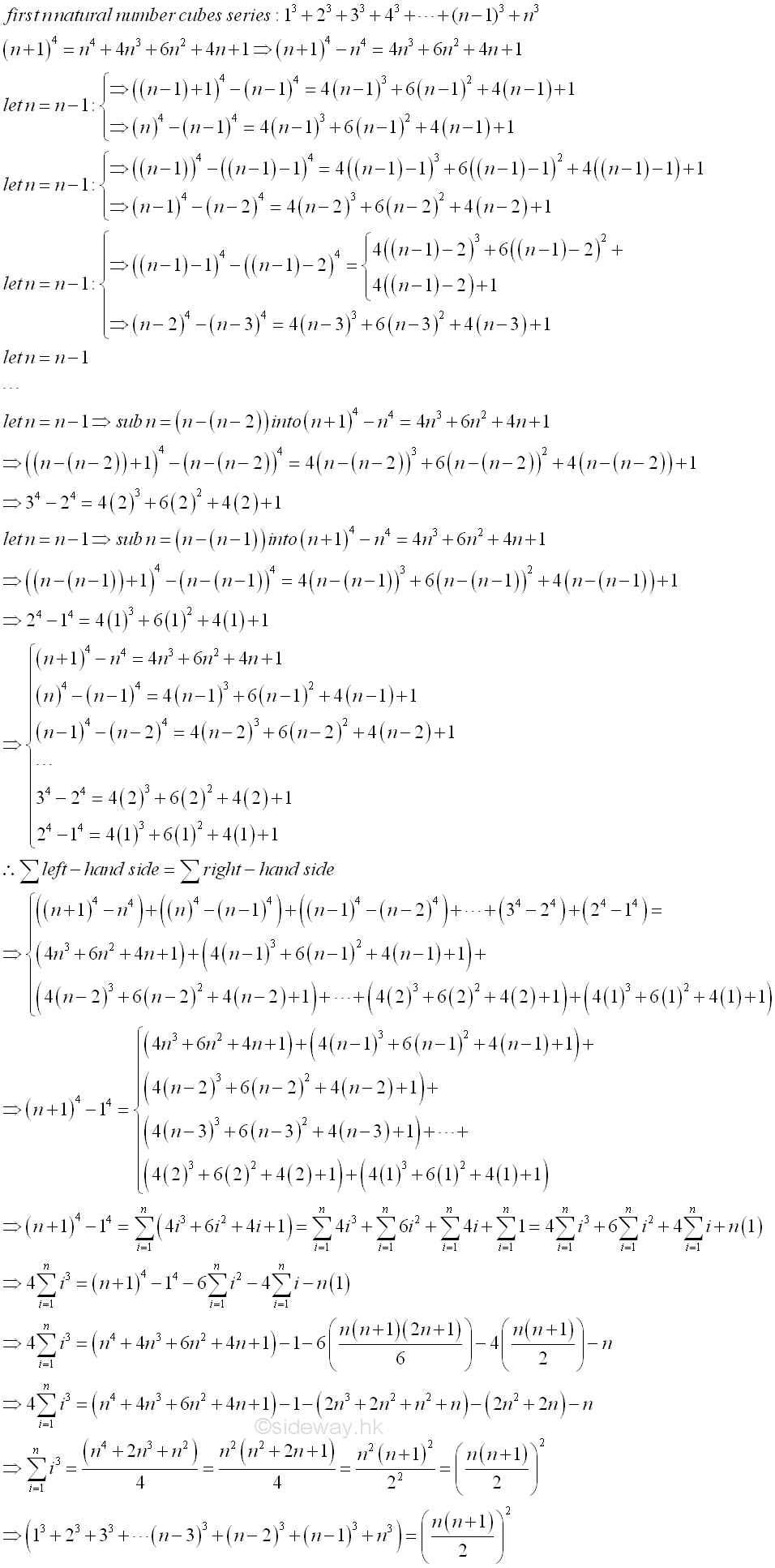
©sideway
ID: 130500021 Last Updated: 5/21/2013 Revision: 0 Ref:
References
- B. Joseph, 1978, University Mathematics: A Textbook for Students of Science & Engineering
- Wheatstone, C., 1854, On the Formation of Powers from Arithmetical Progressions
- Stroud, K.A., 2001, Engineering Mathematics
- Coolidge, J.L., 1949, The Story of The Binomial Theorem
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/10/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight(last updated On 12/6/2025)
- Travel Singapore Rail Network(last updated On 12/5/2025)
- Travel Singapore Things to Know(last updated On 12/4/2025)
- Travel Singapore(last updated On 12/3/2025)
- Legrand Galion(last updated On 12/2/2025)
- Schneider Electric AvatarOn(last updated On 12/1/2025)
- Alfalux(last updated On 11/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 26
Reference 79
Hardware 54
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
