Content
Instantaneous Rate of Change
Flow Rate
Flow Rate Problem
Instantaneous Rate of Change
In linear or circular motion, the instantaneous rate of change is related to the physical displacement of an object with respect to time. But the instantaneous rate of change is also related to the the movement of some quantity passing through a reference with respect to time.
Flow Rate
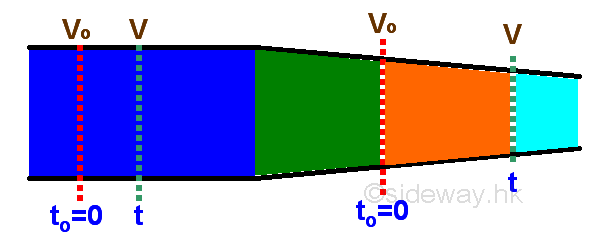
Flow rate usually refer to the volumetric flow rate of an object. Volume flow rate q is defined as the volume of the object passes through a given surface per unit time. When the given surface is equal to one unit, the velocity of the object flow is equal to the magnitude of the volume flow rate.
For a steady flow, the relationship between the final volume V, initial volume Vo, volume flow rate Q and time t can be expressed as a function:
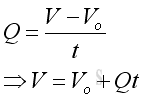
Instantaneous flow rate can be defined as the instantaneous rate of change of the volume flow through a reference with respect to the time t. The derivative of the function is..
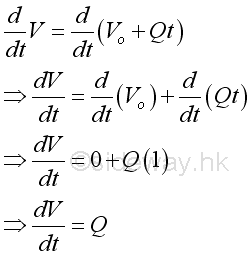
The volume flow rate is a constant for both a steady uniform flow and a steady nonuniform flow because the parameters of the flow do not change in time at every point. However only the uniform flow does have the parameters of the flow are the same for all spatial points along the flow, e.g. flowing through pipe with constant diameter. But for the nonuniform flow, the parameters of the flow vary and are different at different spatial points along the flow, e.g. flowing through a tapering pipe.
For a steady flow with constant acceleration, the relationship between the final volume flow rate Q, initial volume flow rate Qo, acceleration a and time t can be expressed as a function:
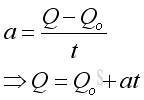
Instantaneous acceleration can be defined as the instantaneous rate of change of the volume flow rate with respect to the time. The derivative of the function is.
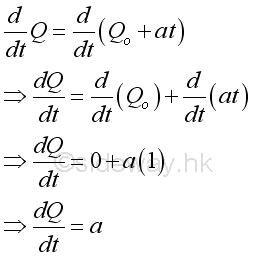
Since V is a function of time f(t), the derivative Q is equal to the first derivative of function V with respect to time t.
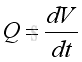
The derivative a is equal to the derivative of function Q with respect to t. But Q is also a function of time, the derivative is

Therefore the derivative a is also equal to the second derivative of function V with respect to t.
Flow Rate Problem
A water supply system is operated by a water pump. The water supply after switching on the pump can be described by a volume function V with respect to time t.
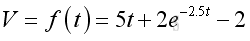
Graphically
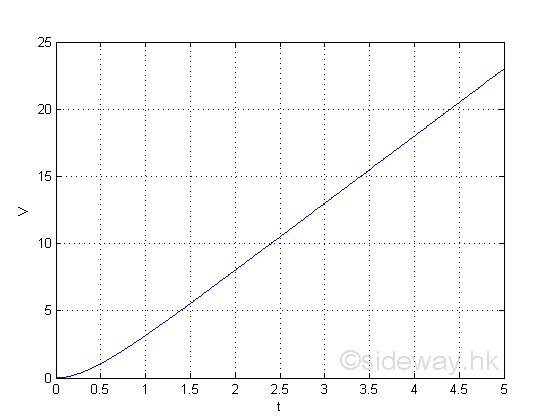
The information directly from the function is the total pumped water.
e.g. at t=1, the total pumped water is 3.1,

e.g. at t=2, the total pumped water is 8,
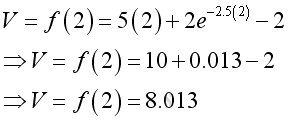
e.g. at t=3, the total pumped water is 13,
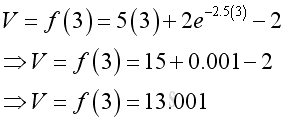
The first derivative can be used to determine the instantaneous volume flow rate. imply

Graphically
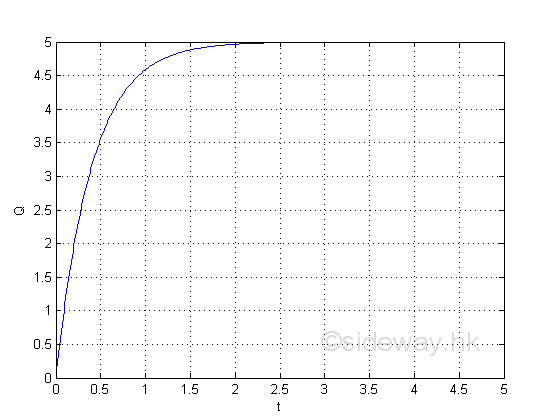
The information directly from the derivative is the instantaneous volume flow rate.
e.g. at t=1, the instantaneous volume flow rate is 4.59
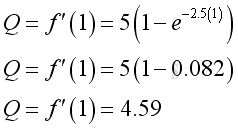
e.g. at t=2, the instantaneous volume flow rate is 4.97.
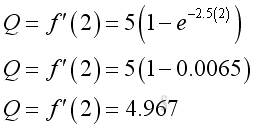
e.g. at t=3, the instantaneous volume flow rate is 5

The second derivative can be used to determine the instantaneous acceleration of the instantaneous volume flow rate. imply

Graphically
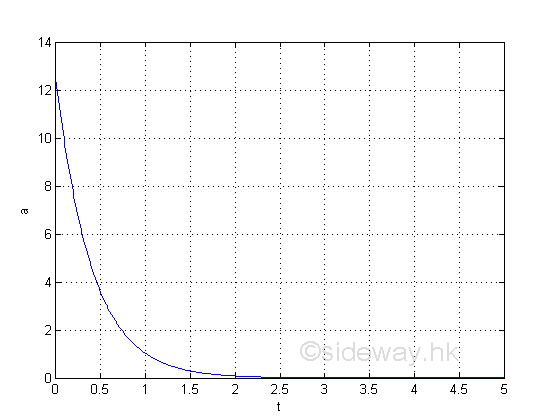
The information directly from the derivative is the instantaneous acceleration.
e.g. at t=1, the instantaneous acceleration is 1.026

e.g. at t=2, the instantaneous acceleration is 0.804
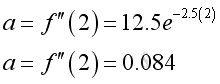
e.g. at t=3, the instantaneous acceleration is 0.007
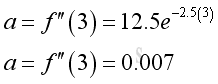
©sideway
ID: 110900016 Last Updated: 9/22/2001 Revision: 0 Ref:
References
- S. James, 1999, Calculus
- B. Joseph, 1978, University Mathematics: A Textbook for Students of Science & Engineering
Latest Updated Links
- Philips CL400 Ceiling Light 13W(last updated On 10/30/2025)
- Ikea TISKEN basket(last updated On 10/29/2025)
- Ikea TISKEN towel rack(last updated On 10/28/2025)
- Ikea REXBEGONIA mattress protector(last updated On 10/27/2025)
- Ikea KEJSAROLVON mattress protector(last updated On 10/26/2025)
- Ikea KVARNVEN ergonomic pillow(last updated On 10/25/2025)
- Ikea BRUKSVARA pocket prung mattress(last updated On 10/24/2025)
- Ikea VÅGSTRANDA pocket sprung mattress super firm(last updated On 10/23/2025)
- Ikea VITVAL underbed(last updated On 10/22/2025)
- Ikea SLÄKT bed frame with slatted bed base(last updated On 10/21/2025)
- ASUS TUF ESD-T1A External SSD Enclosure(last updated On 10/20/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 8
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 18
Reference 79
Hardware 23![]()
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
